From Menus to Multi-Billion Dollar Company: The Zomato Story
How a Simple App Revolutionised the Food Industry in India
When the search for menus turned into a frustrating mess, Deepinder and Pankaj's answer was a brilliant app - 'Zomato.'
In 2008, Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah, who were working at Bain & Company, saw the struggle of finding restaurant menus. That's how FoodieBay, the early Zomato, was born - a digital answer to messy menus.
But Zomato's ambitions grew bigger than just listings. In 2015, they launched food delivery, taking the ordering experience further. They even built their delivery network to ensure smooth service.
Zomato didn't stop there. They created a whole food ecosystem:
Zomato Book (2016): Hassle-free table reservations for a stress-free night out.
Zomato Base (2016): A point-of-sale system for restaurants, streamlining their operations. (Though Zomato Infrastructure Services for cloud kitchens closed in 2018)
Zomato Gold (2017): A membership program for foodies offering discounts and free deliveries.
Zomato's about more than just ordering in! They launched Zomaland, an annual food and entertainment carnival, in 2018.
Fast forward to 2021, Zomato went public with a valuation of over $8 billion! They continued to innovate with features like:
Legends (2022): Order iconic dishes from different cities and deliver them within days.
Zomato Pay (2022): A convenient way to pay at partnered restaurants.
Multi-restaurant ordering (2023): Craving dishes from different places? No problem! Order from up to four restaurants at once.
Zomato’s Products and Vision
Zomato operates across four key business segments, catering to consumers (B2C) and businesses (B2B). Here's a breakdown:
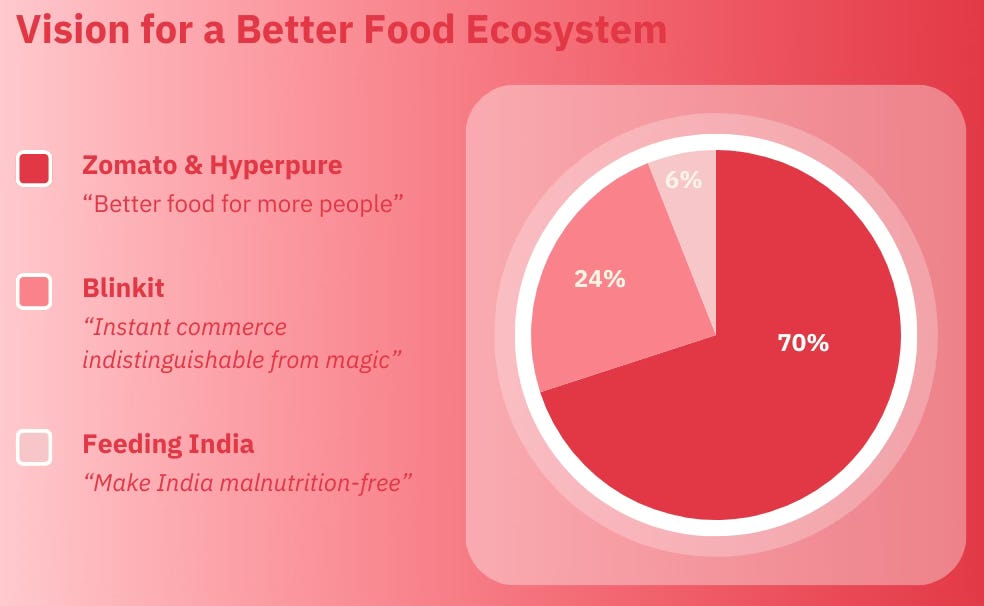
Food Delivery (Launched 2015): Zomato's core business, with a presence in over 800 cities. It contributes the majority (63%) of the company's Gross Order Value (GOV), translating to INR 32,224 Crore.
Quick Commerce (Acquired in 2022): Launched in 2021 through the acquisition of Blinkit, this segment focuses on delivering groceries and essentials within minutes. It operates in 26 cities, contributing 24% (INR 12,469 Crore) to Zomato's GOV.
Dining Out & Zomaland (Launched 2022): This segment facilitates restaurant reservations and promotes food festivals like Zomaland. It operates in 41 cities and contributes 6% (INR 3,225 Crore) to GOV.
Hyperpure (Launched 2019): Zomato's B2B arm, Hyperpure, focuses on directly supplying quality food ingredients and other products to restaurants and other businesses. It also contributes 6% (INR 3,172 Crore) to GOV.
Zomato’s Business Model
Food Delivery and Table Reservation Commissions
One of the main sources of Zomato's revenue generation is the commission charged to restaurants for each order placed on Zomato. When a user orders food from Zomato, the restaurant pays a percentage of the order value to Zomato as the commission. Zomato also earns commissions from restaurants whenever they receive a successful reservation.
Delivery Fees
On top of restaurant commissions, Zomato also charges customers delivery fees for their orders. These fees help Zomato earn more money, and your pay can change depending on how much you order and where you live.
Subscriptions and Advertising
Zomato Gold's subscription program unlocks exclusive discounts and perks for users who pay a monthly fee. While restaurants share some of this revenue, Zomato keeps a portion, boosting their income.
Additionally, Zomato helps restaurants thrive on their platform through targeted advertising and promotions. Restaurants can pay for premium listing placement, design targeted ads to reach specific customers, and offer special deals to attract more orders. These advertising services are significant moneymakers for Zomato.
Events
This multi-city food and entertainment carnival brings together hundreds of restaurants, offering a unique experience for attendees. Zomaland isn't just about delicious food; it features live performances, interactive activities, and exciting attractions, creating a memorable event for all ages. Ticket sales, sponsorships, and vendor fees contribute significantly to Zomato's annual income.
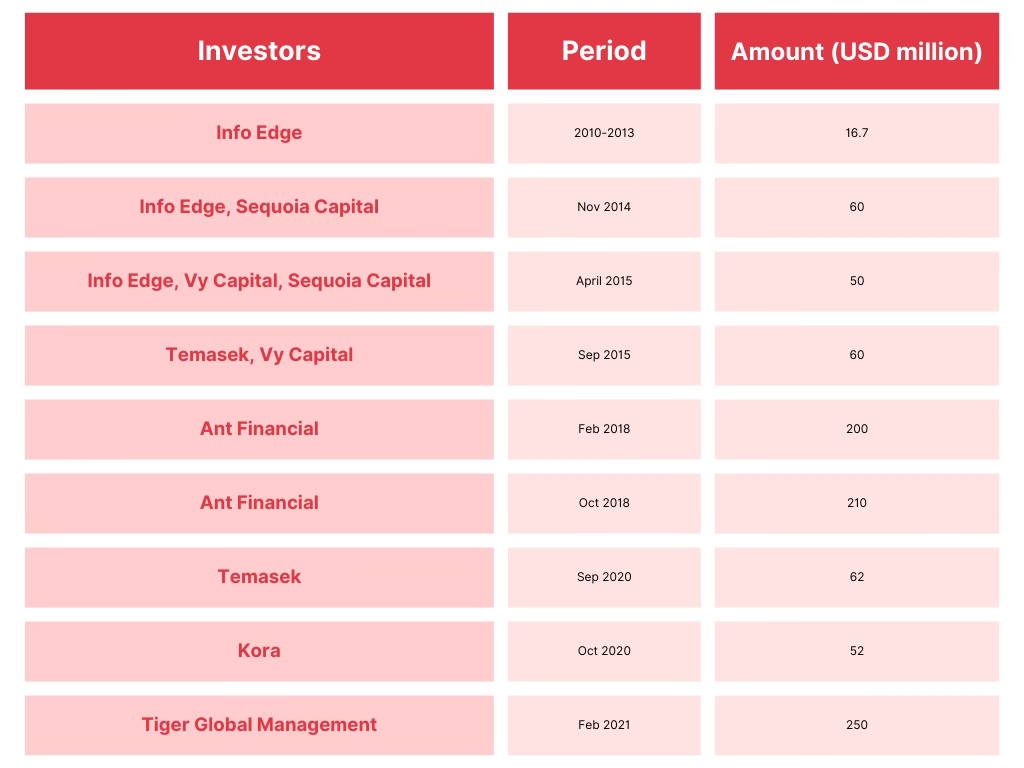
Zomato’s Investors and Acquisitions
Acquisitions
Jan 2015: Acquired Urbanspoon (US & Australia entry), competing with Yelp & Foursquare.
April 2015: Acquired NexTable (US online table reservation platform, renamed Zomato Book).
April 2015: Acquired MapleGraph (cloud-based point of sale system).
2016: Acquired Sparse Labs (renamed Zomato Trace) for real-time delivery tracking.
2018 Acquired WOTU (rebranded Hyperpure): Supplies food ingredients to restaurants.
June 2022: Acquired Blinkit (quick-commerce company) for US$568 million.
Competitive Analysis
Zomato's Commitment to Social Responsibility
Beyond Delivering Great Food, Zomato Makes a Positive Impact.
Fighting Hunger: Zomato partners with Feeding India, an NGO tackling chronic hunger. Their daily feeding programs in 40 cities have served over 170 million meals!
Going Green: Zomato is committed to achieving net zero emissions in its food delivery chain by 2033.
Reducing Plastic Waste: They're dedicated to recycling more than 100% of plastic used in packaging and aim to facilitate 100 million plastic-free deliveries by 2025.
Delivery Partner Wellbeing: Zomato prioritizes its delivery partners' safety. They've trained over 20,000 partners in emergency medical care and provided reflective wear for better nighttime visibility. Additionally, they offer free accidental and medical insurance.